 Most of us have been to the beach and know that seawater is salty. But I’m sure the question of why the sea is like this, may have crossed your mind at some point. Lakes (*except for the Great Salt Lake, Dead Sea, Caspian Sea and other salt lakes that have no outlets), ponds and rivers for example are not salty and even the rain that comes from above is fresh water.
Most of us have been to the beach and know that seawater is salty. But I’m sure the question of why the sea is like this, may have crossed your mind at some point. Lakes (*except for the Great Salt Lake, Dead Sea, Caspian Sea and other salt lakes that have no outlets), ponds and rivers for example are not salty and even the rain that comes from above is fresh water. Oceans cover about 70% of the earth's surface with water and from this 3 % is fresh water. Two-thirds of this fresh water is in a solid state (frozen) in glaciers and icecaps. The other 1 percent of this is found in clouds, precipitation (rain and snow), rivers, ponds, lakes and underground water. Seawater has a salinity of 3.5% (35 parts per thousand). In other words, about 35 of 1,000 (3.5%) of the weight of seawater comes from the dissolved salts. This is the amount of salt in the world's oceans. Thus, for every 1 liter of sea water there are 35 grams of salts. Most of the sea's salt is sodium chloride (NaCl) - common table salt - (technically it is called halite) which is dissolved in it. This dissolved salt is made of two ions; chloride and sodium ions
Oceans cover about 70% of the earth's surface with water and from this 3 % is fresh water. Two-thirds of this fresh water is in a solid state (frozen) in glaciers and icecaps. The other 1 percent of this is found in clouds, precipitation (rain and snow), rivers, ponds, lakes and underground water. Seawater has a salinity of 3.5% (35 parts per thousand). In other words, about 35 of 1,000 (3.5%) of the weight of seawater comes from the dissolved salts. This is the amount of salt in the world's oceans. Thus, for every 1 liter of sea water there are 35 grams of salts. Most of the sea's salt is sodium chloride (NaCl) - common table salt - (technically it is called halite) which is dissolved in it. This dissolved salt is made of two ions; chloride and sodium ions 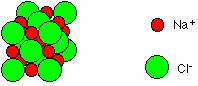 (Na+ and Cl-). This makes up about 78 percent of the total dissolved chemical substances in seawater. Seawater is a complex solution with trace (smaller ) amounts of other chemical elements such as potassium, magnesium, sulfur, and calcium just to name a few. Thus, seawater contains a variety of salts.
(Na+ and Cl-). This makes up about 78 percent of the total dissolved chemical substances in seawater. Seawater is a complex solution with trace (smaller ) amounts of other chemical elements such as potassium, magnesium, sulfur, and calcium just to name a few. Thus, seawater contains a variety of salts.Interestingly it may surprise you to know that fresh water, strictly speaking, is not entirely free of dissolved salt. So, rivers, ponds, most lakes and rainwater has some traces of dissolved chemical substances. However the amount is so small (concentration is too low) that it will not be detected by just tasting it. Rainwater picks up traces of dissolved substances during its passage through the atmosphere.
How the Ocean becomes Salty - Why is Seawater salty?
When rain falls, it dissolves carbon dioxide from the surrounding air. This therefore causes the rainwater to be slightly acidic due to carbonic acid. That is, carbonic acid is formed from carbon dioxide dissolving into the rainwater. When this rain water falls to the earth and passes through soil and percolates through rocks, the acid erode the rocks and breaks down the rocks (dissolving some of its minerals) and carries it along its path in a dissolved state as ions. This process is know as weathering. This rainwater with its ions (dissolved minerals/salts) eventually are carried to the streams, rivers and lakes into the ocean.
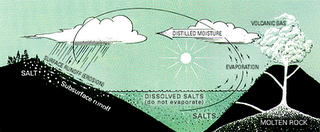 Click to enlarge image
Click to enlarge imageThe oceans also receive salts (dissolved mineral ions) through submarine volcanism. That is, from the eruption of volcanoes under the oceans floor bed . This process is similar to the rainwater in that it is reacting with hot molten rock and dissolving some of the mineral constituents. Dissolved mineral ions also comes from the solid and gaseous materials that escaped from the Earth's crust through volcanic vents above the oceans. This is swept from the land to the ocean by offshore winds, and through runoffs from rainfall that dissolve these minerals. Also, some of the sea's salts comes from rocks and sediments dissolved from below its floor. This comes from the ocean floor at places called hydrothermal vents that erode (dissolve) the rocks of the oceanic crust of its constituents (minerals) when it becomes hot thus, adding to the sea’s salt content.
 This accumulation of dissolved salts left over very long periods of time increases in its concentrations. The salinity is also increased by evaporation or by freezing of sea ice thus, making it more salty. However, the salinity of the oceans is in a steady state which is due to: many dissolved ions that are used (removed) by marine life, the formation of new minerals at the bottom of the ocean, rainfall, runoff, or the melting of ice which decreases its salinity.
This accumulation of dissolved salts left over very long periods of time increases in its concentrations. The salinity is also increased by evaporation or by freezing of sea ice thus, making it more salty. However, the salinity of the oceans is in a steady state which is due to: many dissolved ions that are used (removed) by marine life, the formation of new minerals at the bottom of the ocean, rainfall, runoff, or the melting of ice which decreases its salinity.It is worth noting that sea water salinity is not uniform throughout the world. There are sea water located in the eastern sections of Gulf of Finland and in the northern end of Gulf of Bothnia that have seawater with the least salinity compared to other parts of the world. Both these sections are of the Baltic Sea. On the other hand, the most saline open sea is the Red Sea. A long narrow sea between northeast Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. It is linked with the Gulf of Aden and the Arabian Sea by the straits of Bab el Mandeb. The factors responsible for this sea to be most saline is caused by confined circulation and high temperatures. Due to the confined circulation, there is little fresh inflow of water from rivers and along with its high temperature, this causes high rates of surface evaporation. This combines to give the Red Sea a high saline (salty) content in comparison to others.
 *Salt lakes such as the Great Salt Lake, Caspian Sea and the Dead Sea are salty (about 10 times saltier than sea water) because they have no outlets like other lakes where water flows in at one end by rivers and streams and out the other end by rivers. This therefore means that all the water that flows into these lakes escapes only by evaporation. So, when this process of evaporation takes place there will be less water content and a higher concentration of salts. Thus, large amounts of dissolved salts remain in the lake.
*Salt lakes such as the Great Salt Lake, Caspian Sea and the Dead Sea are salty (about 10 times saltier than sea water) because they have no outlets like other lakes where water flows in at one end by rivers and streams and out the other end by rivers. This therefore means that all the water that flows into these lakes escapes only by evaporation. So, when this process of evaporation takes place there will be less water content and a higher concentration of salts. Thus, large amounts of dissolved salts remain in the lake.Photo showing the Caspian Sea viewed from orbit. Click to enlarge image.
Related Articles:
What happens to marine life when a lake or pond is frozen?
How Do Fish Breathe?
these are good facts.
ReplyDeletedoes anyone even come on your site?
ReplyDelete... anyway, these are good facts... again..
One question....
ReplyDeleteif salinity is 3.5% by weight
then shouldn't it be that
"for every 1 kg ( instead of 1 litre that u have written) of sea water there is 35 grams of salt"
Very good observation. But in this case it's relevant to use liters because the density of water is exactly 1g/cm³. Since 1 cm³ is equal to 1ml. Using liters In the case of any other element, would not be practical.
DeleteI didn't know why, so thanks for the info, but I knew that for this reason, being salty, sea water is healthy for us, people.
ReplyDeleteThis Blog is going places, the people, the layout, amazing to see such dedication and focus.
ReplyDelete