 I am sure you have wondered and ask the question sometime in your life: Why is the sky blue? The sky is black at night with “dots” of stars scattered over the sky while, in the day the sky is blue without the view of a star. What could be the cause of this phenomenon? Well that will be answered today.
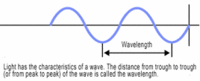
I am sure you have wondered and ask the question sometime in your life: Why is the sky blue? The sky is black at night with “dots” of stars scattered over the sky while, in the day the sky is blue without the view of a star. What could be the cause of this phenomenon? Well that will be answered today.First to understand why the sky is blue, you will need to know that light is made up of a spectrum of colors that exhibits the characteristics of a wave. To be more specific, white light ( e.g. the Sun’s light) is made up of wavelengths of different colors of light. This phenomenon can be explained (and was demonstrated by mathematician and scientist Sir Isaac Newton 1642-1727) by letting a beam of sunlight (white light ) passing through a prism.
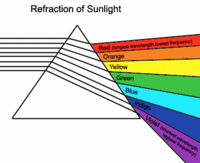
 When white light passes through a prism, it scatters the different colors of light according to their wavelength, showing a continuous band of colors. This band of colors appears in the same pattern as the colors of a rainbow. This means, all the different colors of light (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet) combine to give you what is called white light. These colors, base on their wavelength, are arranged in the order shown above when they are being scattered. The longest wavelengths of light are on the red end of the spectrum and the shortest wavelengths are on the violet end of the spectrum.
When white light passes through a prism, it scatters the different colors of light according to their wavelength, showing a continuous band of colors. This band of colors appears in the same pattern as the colors of a rainbow. This means, all the different colors of light (red, orange, yellow, green, blue, indigo and violet) combine to give you what is called white light. These colors, base on their wavelength, are arranged in the order shown above when they are being scattered. The longest wavelengths of light are on the red end of the spectrum and the shortest wavelengths are on the violet end of the spectrum.When sunlight enters our atmosphere it collides with water molecules, dust particles and gases (oxygen atoms from oxygen (O2) and nitrogen atoms from nitrogen (N2) ) which scatter (Rayleigh scattering) the light around the sky.
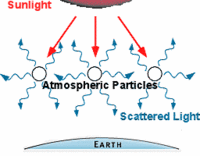 Here, the light with the shorter wavelength is scattered more by this collision than light with longer wavelengths. In this case, violet light is scattered the most, but human eyes do not see this color very well. However, since the human eyes are more sensitive to blue light (the next most scattered visible color), you will see the sky as blue. You will also notice that closer to the horizon, the sky appears much paler in color. This is due to the scattered blue light passing through more air particles in the atmosphere to reach you, from that angle.
Here, the light with the shorter wavelength is scattered more by this collision than light with longer wavelengths. In this case, violet light is scattered the most, but human eyes do not see this color very well. However, since the human eyes are more sensitive to blue light (the next most scattered visible color), you will see the sky as blue. You will also notice that closer to the horizon, the sky appears much paler in color. This is due to the scattered blue light passing through more air particles in the atmosphere to reach you, from that angle.Hence, the blueness of the sky is from the blue light that is scattered from the sunlight in the atmosphere which, then enters our eyes from all regions of the sky.
 The black sky at night that shows you the stars in space is due to the absences of the Sun’s light. There is no scattered light to reach the eyes of an observer during the night. Where there is no light there is darkness. So, the sky is black during the night revealing outer space. It is also important to note that, the moon does not gives its own light and the reflected light is not strong to have the same effect as the Sun.
The black sky at night that shows you the stars in space is due to the absences of the Sun’s light. There is no scattered light to reach the eyes of an observer during the night. Where there is no light there is darkness. So, the sky is black during the night revealing outer space. It is also important to note that, the moon does not gives its own light and the reflected light is not strong to have the same effect as the Sun.Sunrise and Sunset

You might ask, what about the color of a sunrise or sunset? Well, basically the same principle applies here. During sunrise and sunset the distance that the sunlight has to travel through the atmosphere to an observer is much greater. This is, as a result of, the Sun being almost in line with the horizon unlike, in the day when it is higher in the sky. This means, there are now more molecules to efficiently scatter the violet and blue light along a greater distance since, they have the shortest wavelength light in the spectrum. Therefore, all of the blue and violet light get scattered (redirected) out of your line of sight leaving the light of the longer wavelength. Thus, the unhindered the light of longer wavelength that consist of the colors; red, orange and yellow will reach the eyes of the observer. These light of different colors coming from the direction of the Sun through the atmosphere directly to you, are responsible for coloration of the sunrise and sunset. Note also that, the entire sky does not become red, orange or yellow because these light remain unhindered in their path and do not scatter over the sky in different directions.
So, next time when you are enjoying or taking a picture of the sunset, you will now know the principle behind such splendid beauty.
Here are some bonuses
Did you know that the Sun is white in outer space and not yellow?

In space, there is no atmosphere so, there are no particles to scatter the Sun’s white light into different colors of light in the visible spectrum. Therefore, space being a vacuum, the sunlight will remain as a white light until it hits the Earth’s atmosphere, where the scattering effect then begins. This is why the Sun looks white in space. If you were observing from the moon, the Sun would look white just the same because the moon does not have an atmosphere.
Do you know the reason why clouds are white?
Cloud particles (large water droplets or ice particles) reflect ( scatter) all visible wavelengths of light equally thus, causing the white appearance of clouds. This type of scattering is called Mie Scattering (for particle sizes larger than a wavelength).
On the other hand, clouds can also appear dark in appearance taking on the color grey or black. The explanation for this is that clouds can become very thick or dense which cause less or no sunlight passing through them.
Hence, the color of clouds will therefore depend on the amount of sunlight passing through it, in relation to the thickness of the cloud.
Related Articles:
How Are Rainbows Formed?
The Meaning of Colors - Color Symbolism
Why are traffic lights Red, Yellow and Green?
Why leaves change color in fall?
What causes hair to turn gray?
Why do people have different colors of skin?
Excellent! You are so blog-rolled! Thank you.
ReplyDeleteYou are welcome and thank you very much Doris:0)
ReplyDeleteDear Prof,
ReplyDeleteMerci beaucoup!
Why not turn "DO YOU KNOW WHY THE SKY IS BLUE?" into a fully illustrated in colour book for children to learn all these Chemistry and Physics?