 Those of us that live in temperate countries have the luxury of admiring one of nature's beauties every fall (autumn) - the beauty of the trees all covered with leaves of different colors. The clear, beautiful blue sky steering down from above while below the landscape it is all dotted with a variety of trees showing off their splendid leaves of different colors thus, making an awesome scenery of nature in a clean, fresh cool air of fall.
Those of us that live in temperate countries have the luxury of admiring one of nature's beauties every fall (autumn) - the beauty of the trees all covered with leaves of different colors. The clear, beautiful blue sky steering down from above while below the landscape it is all dotted with a variety of trees showing off their splendid leaves of different colors thus, making an awesome scenery of nature in a clean, fresh cool air of fall.Did you ever wonder how and why this happens? Most of us, no doubt, know that the changing of the leaves color have something to do with the climate. After all, the leaves of different trees do change color at this season each time every year. So, how do we explain this phenomena of what causes leaves to change their colors? Well, to explain this first we will need to take a quick look on the structure and function of a normal leaf.
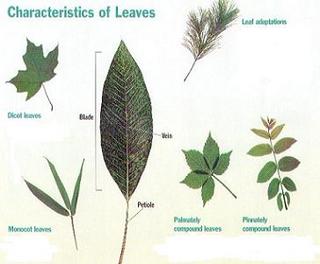
A leaf is an outgrowth of a plant that grows from a node in the stem. Most leaves are flat, or broad, and come in various shapes and sizes, some of which can be: blade shaped, oval, round, feathery and so on. For leaves that are of conifers (cone-bearing trees), they are usually small and needlelike in shape. Leaves are usually green in color which is due to a green pigment called chlorophyll inside the leave.
 This green pigment Chlorophyll, absorbs mainly violet-blue and orange-red light. The other color green that makes up the sun’s light (white light) is therefore scattered from the surface of the leaf.
This green pigment Chlorophyll, absorbs mainly violet-blue and orange-red light. The other color green that makes up the sun’s light (white light) is therefore scattered from the surface of the leaf.  Because chlorophyll absorb the wavelengths of visible light ( violet-blue and orange-red light) and scatter (reflect) the green light that eventually reaches our eyes, chlorophylls therefore appears green in color . Thus, due to the great abundance of chlorophyll in leaves, this causes leaves to look green in color. There are however, other pigments present inside the leaf of a plant called carotenoids and Anthocyanins. Carotenoids pigment gives the color yellow, orange, and brown hues. Anthocyanins gives the color red, purple, and crimson. These pigments are present in leaves but are in small numbers due to a warm and sunny climate condition. Under such conditions the colors of carotenoids are masked by the great abundance of green chlorophyll during these conditions. Chlorophyll dominate in number during these warm and sunny ( growing season) conditions because of the role they play in photosynthesis. Most anthocyanins however, are produced in autumn in response to the bright light and excess plant sugars (glucose) within the plant leaf cells.
Because chlorophyll absorb the wavelengths of visible light ( violet-blue and orange-red light) and scatter (reflect) the green light that eventually reaches our eyes, chlorophylls therefore appears green in color . Thus, due to the great abundance of chlorophyll in leaves, this causes leaves to look green in color. There are however, other pigments present inside the leaf of a plant called carotenoids and Anthocyanins. Carotenoids pigment gives the color yellow, orange, and brown hues. Anthocyanins gives the color red, purple, and crimson. These pigments are present in leaves but are in small numbers due to a warm and sunny climate condition. Under such conditions the colors of carotenoids are masked by the great abundance of green chlorophyll during these conditions. Chlorophyll dominate in number during these warm and sunny ( growing season) conditions because of the role they play in photosynthesis. Most anthocyanins however, are produced in autumn in response to the bright light and excess plant sugars (glucose) within the plant leaf cells.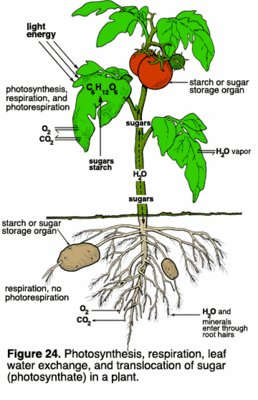 Plants manufacture their own food for their own survival by using their leaves. This they achieve by using the pigment Chlorophyll. Chlorophyll’s function is to absorb the light ( violet-blue and orange-red light) necessary for their food production by converting energy from sunlight into chemical energy (food) through a process called Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants (using chlorophyll) synthesize carbohydrates (food) from carbon dioxide and water using light (sun) as an energy source. Plants take up water from the ground through their roots ( by a process called Osmosis) and send it to their leaves (the food manufacturing site) while simultaneously, the leaves take the gas carbon dioxide ( CO2 ) from the air ( by a process called Diffusion) and with the energy from the sunlight manufacture their food.
Plants manufacture their own food for their own survival by using their leaves. This they achieve by using the pigment Chlorophyll. Chlorophyll’s function is to absorb the light ( violet-blue and orange-red light) necessary for their food production by converting energy from sunlight into chemical energy (food) through a process called Photosynthesis. Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants (using chlorophyll) synthesize carbohydrates (food) from carbon dioxide and water using light (sun) as an energy source. Plants take up water from the ground through their roots ( by a process called Osmosis) and send it to their leaves (the food manufacturing site) while simultaneously, the leaves take the gas carbon dioxide ( CO2 ) from the air ( by a process called Diffusion) and with the energy from the sunlight manufacture their food.sunlight
Carbon dioxide (gas) + water ------------> glucose (sugar) + oxygen (gas)
Chlorophyll
For those of you that need the extra knowledge. Here is the chemical equation for the above word equation:
light energy from sun
6CO2 + 6H2O ----------------------------> C6 H12 O6 + 6O2
Chlorophyll
Now, we are now in a much better position to answer the question “what causes leaves to change color in fall?” There are more than one factors that are responsible or influence the amount of colors found in leaves during fall. These include: rain, amount of sugar in the leaves, wind and temperatures. As summer ends and fall (autumn) begins the length of daylight gets shorter as one goes further into fall with the change in temperature. When this happens there will be less sunlight present, lower temperature and as a result, less chlorophyll reproduction that is needed for Photosynthesis to take place. At the same time the chlorophyll already present begins to break down. Because of this, chlorophyll starts to diminish thus, the carotenoids pigment gradually become more dominant.
 Consequently, the leaves start to take the color of the pigment that is now more dominant. When all the chlorophyll are diminished the leaves will have no green color. During this time also, lots of sugars (glucose) are produced in the leaf but the cooler temperature during the nights along with the gradual closing of veins that goes into the leaf prevent these sugars from moving out. This shutting down of their food production happens because of the absence of chlorophyll. Trees will now have to live off the food they stored during the summer in their roots, bark and other parts of the plant. This condition favors and causes the production of anthocyanin pigments. The carotenoids pigment already in the leaves and the anthocyanin pigment provides a brilliant and awesome spectrum of colors that manifest itself in the leaves.
Consequently, the leaves start to take the color of the pigment that is now more dominant. When all the chlorophyll are diminished the leaves will have no green color. During this time also, lots of sugars (glucose) are produced in the leaf but the cooler temperature during the nights along with the gradual closing of veins that goes into the leaf prevent these sugars from moving out. This shutting down of their food production happens because of the absence of chlorophyll. Trees will now have to live off the food they stored during the summer in their roots, bark and other parts of the plant. This condition favors and causes the production of anthocyanin pigments. The carotenoids pigment already in the leaves and the anthocyanin pigment provides a brilliant and awesome spectrum of colors that manifest itself in the leaves.Other weather factors such as rain (water) and wind also influence the color of leaves along with the duration of their color. The frequency in rainfall provides a soil that is well moist and a humid atmosphere. These two conditons provide a cooler temperature that will further favor anthocyanin formation. If the weather condition is windy, this will then provide a further cooling effect through evaporation thus, providing a cooling effect that favors anthocyanin formation. This give the leaves a further bright red, purple and crimson color. It is also possible for color changes to be delayed if their was a severe summer drought before the beginning of winter. Freezing temperatures usually lower the color intensity of the leaves during fall and as winter approaches. It is also important to note, that the color of leaves usually go with the type of tree it is from. This means, different types of trees give a certain variety of colors - an hereditary information that is pass down from the same type of tree. So you will find trees that are more reddish or trees with leaves that are more brightly yellow and so on. Here are some examples of trees that give specific colors based on their type:
 Red - sumac, tupelos, some oaks and maples.
Red - sumac, tupelos, some oaks and maples.Red or yellow - dogwood, sourwood, sugar maple, black gum, and sweet gum.
Orange - some oaks and maples.
Yellow - Ash, basswood, beech, birch, butternut, elm, hickory, some maples (e.g. silver, striped, and sugar), mountain ash, poplar, redbud, serviceberry, and willow.
 So, take the time to enjoy one of nature’s beauties - the splendid variety of colors from trees of different type. Take a trip to the hills, park or to the country where you can take pictures and be at one with nature. After all, fall only comes once a year.
So, take the time to enjoy one of nature’s beauties - the splendid variety of colors from trees of different type. Take a trip to the hills, park or to the country where you can take pictures and be at one with nature. After all, fall only comes once a year.Related Articles:
How Rainbows Are Formed - What Causes a Rainbow?
The Meaning of Colors - Color Symbolism
Why are traffic lights Red, Yellow and Green?
What causes hair to turn gray?
Why do people have different colors of skin?
Why is the sky blue?
A few minutes of mine very well spent.
ReplyDeleteThanks once again
Hi,
ReplyDeleteJust dropping by to say hello.
Enviroman Says
I did not know that , Thank you for sharing ,I enjoyed your blog ,
ReplyDeleteSam I am
Did You Know?
ReplyDeleteShould be compiled into a book in volumes and published every year as a handy book for homes and schools.
That's pretty cool! Thanks for the info...I didn't even know that I wanted to know that...
ReplyDeleteIntorduced! on BlogIntro.com
ReplyDeleteThank you guys for much for your comments.
ReplyDeleteFor those of you that are coming here for the first time, I will be visiting your site.
Thanks again.
I needed help on my homework about way leaf change colors on fall and I found all the answers to my homework. This really helps a lot. Now i know. Thank you!
ReplyDeletei hate this web site bitches fuck u ugly holes!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
ReplyDeletethanks for the info
ReplyDeleteI like to suggest that the statement "hereditary information that is "pass" down; should be changed to "passed" down. This will give the sentence the proper tense. Thanks
ReplyDelete