How are we able to see things?
 The human eye is a extremely sophisticated visual anatomical device ( sensory organ) architecturally designed elegantly and efficiently for its purpose. Our eyes are the window to this world that allow us to see its spectacular beauty. Through our eyes we see places, objects, friends, family, our own body, our pets and other living things around us. It allows us to see, interpret, make decisions and conclusions about things we see. Through our eyes we can tell if something is beautiful, ugly, colorful, dull, rough, smooth, glossy, bright, dark, transparent, as dimensions and so on. Also, it allows us to; learn from visual information, compare, contrast and make decisions. Our eyes serve as a protection device that protect us from harm by allowing us to make judgment or prediction of an object or event and to take the necessary action (response) of whether to fight or flee. Through our eyes we also communicate with each other and send message to others about our
The human eye is a extremely sophisticated visual anatomical device ( sensory organ) architecturally designed elegantly and efficiently for its purpose. Our eyes are the window to this world that allow us to see its spectacular beauty. Through our eyes we see places, objects, friends, family, our own body, our pets and other living things around us. It allows us to see, interpret, make decisions and conclusions about things we see. Through our eyes we can tell if something is beautiful, ugly, colorful, dull, rough, smooth, glossy, bright, dark, transparent, as dimensions and so on. Also, it allows us to; learn from visual information, compare, contrast and make decisions. Our eyes serve as a protection device that protect us from harm by allowing us to make judgment or prediction of an object or event and to take the necessary action (response) of whether to fight or flee. Through our eyes we also communicate with each other and send message to others about our  present state. For example, we use our eyes to send a message to someone if we are in agreement with the action they are doing or about to do by blinking (winking) one of our eyes. We can also use ours eyes tell someone we are interested in them or you can receive a message if someone is interested in you.Through the eyes we can read messages about the persons state or mood
present state. For example, we use our eyes to send a message to someone if we are in agreement with the action they are doing or about to do by blinking (winking) one of our eyes. We can also use ours eyes tell someone we are interested in them or you can receive a message if someone is interested in you.Through the eyes we can read messages about the persons state or mood  such as if they are; sad, tired, stressed, ill, drunk, frustrated, crying, happy, angry, surprised, depress, excited, sleepy and so on. Thus, like most people we depend on
such as if they are; sad, tired, stressed, ill, drunk, frustrated, crying, happy, angry, surprised, depress, excited, sleepy and so on. Thus, like most people we depend on our eyes to carry out our busy daily activities but have you ever wondered or stop to think how incredible this wonderful and special designed organ allows you to see and also to read this article? Let's take a look on the anatomy and function of the eye to see how it works and also how important your vision is to you.
our eyes to carry out our busy daily activities but have you ever wondered or stop to think how incredible this wonderful and special designed organ allows you to see and also to read this article? Let's take a look on the anatomy and function of the eye to see how it works and also how important your vision is to you.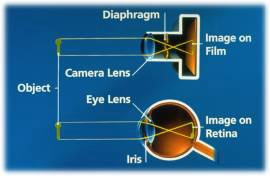 How the eye works can be compared to that of a simple camera. Like the eye, a camera creates images by focusing (using the cornea and lens) on an object by allowing certain amounts of light (reflected from the object) to pass through a hole ( iris and diaphragm) that adjusts the amount of light entering which then creates a visual impression (on the retina and on film). The light can originate directly either from the object (e.g. the sun, bulb) or in directly from an object (a chair, book, moon) by the reflected light from its surface. This explains why we can’t see in the dark. Darkness is the absent of light thus, there is no light reflected from the object to enter through our pupil to form an image on our retina in the eye. If there is light we are able to see the object depending on the amount of light present. The limited amount of light in a dark room for example, can also let us see things without colors giving a dull, dark, grayish appearance (see retina section on rods for reason, further down below). The colors we see when we look at objects are due to the light source and also from the light that is reflected from that object to the eye.
How the eye works can be compared to that of a simple camera. Like the eye, a camera creates images by focusing (using the cornea and lens) on an object by allowing certain amounts of light (reflected from the object) to pass through a hole ( iris and diaphragm) that adjusts the amount of light entering which then creates a visual impression (on the retina and on film). The light can originate directly either from the object (e.g. the sun, bulb) or in directly from an object (a chair, book, moon) by the reflected light from its surface. This explains why we can’t see in the dark. Darkness is the absent of light thus, there is no light reflected from the object to enter through our pupil to form an image on our retina in the eye. If there is light we are able to see the object depending on the amount of light present. The limited amount of light in a dark room for example, can also let us see things without colors giving a dull, dark, grayish appearance (see retina section on rods for reason, further down below). The colors we see when we look at objects are due to the light source and also from the light that is reflected from that object to the eye.
Click All Image To Enlarge
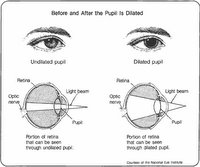 In order to see an object light must first come from the object or bounce off the surface of that object and then enter our eyes. When light reaches our eyes it enters through a transparent layer of tissue called the cornea (the window of the eye). The cornea, responsible for focusing, takes widely diverging rays of light reaching the eyes and converge (bends) them through the pupil. The pupil is the black-appearing round spot (opening) in the center of the colored iris that regulates how much light enters the eye by expanding and contracting its opening. For example, if you are in a room with low lighting, the pupil will expand to allow more light to enter, likewise, if the light is too bright, the pupil will contract (shrink) to allow more light to enter the eye in order to vision the surrounding. Here, the pupil prevent damage to be done to the eyes from excess light entering. You can try this with a friend, spouse or a family remember by staying in the dark for awhile then let some look at your pupil then repeat this the other way around by staying in a bright light or bright sun then let someone looks at your pupil. Do you ever feel a slight pain and temporary blindness when you ever move from a dark surrounding to a well lit surrounding? This happens because too much lights enters the eyes and the pupil quickly adjust the pupil size to limit the amount of light entering the eye - then that temporary blindness will then all go away.
In order to see an object light must first come from the object or bounce off the surface of that object and then enter our eyes. When light reaches our eyes it enters through a transparent layer of tissue called the cornea (the window of the eye). The cornea, responsible for focusing, takes widely diverging rays of light reaching the eyes and converge (bends) them through the pupil. The pupil is the black-appearing round spot (opening) in the center of the colored iris that regulates how much light enters the eye by expanding and contracting its opening. For example, if you are in a room with low lighting, the pupil will expand to allow more light to enter, likewise, if the light is too bright, the pupil will contract (shrink) to allow more light to enter the eye in order to vision the surrounding. Here, the pupil prevent damage to be done to the eyes from excess light entering. You can try this with a friend, spouse or a family remember by staying in the dark for awhile then let some look at your pupil then repeat this the other way around by staying in a bright light or bright sun then let someone looks at your pupil. Do you ever feel a slight pain and temporary blindness when you ever move from a dark surrounding to a well lit surrounding? This happens because too much lights enters the eyes and the pupil quickly adjust the pupil size to limit the amount of light entering the eye - then that temporary blindness will then all go away.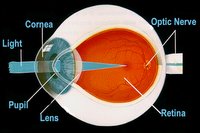
 When the light goes through the pupil it then passes through the lens, a transparent structure situated behind the pupil of the eye, then refract the incoming light and fine tune the focused light onto the retina. This it does by changing the focus of the light from distant objects by altering its shape. This change in focus is called accommodation. You can alter the focus of your lens by placing your finger in front of your face and slowly bringing your finger closer to eyes, right up to your nose then move it away again - there you have just altered your focus by altering the lens of your eyes. This focus light will then travel through the vitreous humour (a clear gel) that fills the central core of the eye and helps to maintain the eye spherical shape.
When the light goes through the pupil it then passes through the lens, a transparent structure situated behind the pupil of the eye, then refract the incoming light and fine tune the focused light onto the retina. This it does by changing the focus of the light from distant objects by altering its shape. This change in focus is called accommodation. You can alter the focus of your lens by placing your finger in front of your face and slowly bringing your finger closer to eyes, right up to your nose then move it away again - there you have just altered your focus by altering the lens of your eyes. This focus light will then travel through the vitreous humour (a clear gel) that fills the central core of the eye and helps to maintain the eye spherical shape.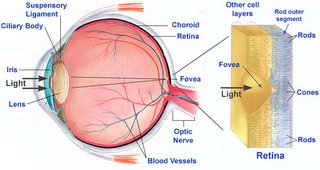 After leaving the lens and traveling through the vitreous humour it will then reach the retina which is at the back of the eye. The retina is a light-sensitive membrane lining the inner wall of the eyeball. This contains millions of photoreceptor nerve cells which react to the presence and intensity of the light image. There are two types of photoreceptors which are called rods and cones. [image here] The rods register shapes and respond to low levels of light which is responsible for night vision while, on the other hand, the cones register (detect) color and only work in bright light. This means when there is less light or as the evening becomes darker the cones will become less responsive and thus, it is more difficult to see colors.
After leaving the lens and traveling through the vitreous humour it will then reach the retina which is at the back of the eye. The retina is a light-sensitive membrane lining the inner wall of the eyeball. This contains millions of photoreceptor nerve cells which react to the presence and intensity of the light image. There are two types of photoreceptors which are called rods and cones. [image here] The rods register shapes and respond to low levels of light which is responsible for night vision while, on the other hand, the cones register (detect) color and only work in bright light. This means when there is less light or as the evening becomes darker the cones will become less responsive and thus, it is more difficult to see colors.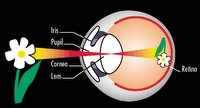 When the light image hits the retina an image will form upside down on its membrane surface containing the photoreceptors cells (light-sensitive cells). The image will then form upside down because the light rays cross while going through the cornea. This will then stimulate the photoreceptors cells (rods and cones) to change the light image into an electrochemical impulse (signals) which then travels along the optic nerve (bundle of retinal fibers )that exits the back of the eye to the vision center (occipital cortex) of the brain. Here the brain interprets the electrical signal and re-adjust the image upward allowing us to “see” the object. Hence, sight (vision) is achieved in the brain.
When the light image hits the retina an image will form upside down on its membrane surface containing the photoreceptors cells (light-sensitive cells). The image will then form upside down because the light rays cross while going through the cornea. This will then stimulate the photoreceptors cells (rods and cones) to change the light image into an electrochemical impulse (signals) which then travels along the optic nerve (bundle of retinal fibers )that exits the back of the eye to the vision center (occipital cortex) of the brain. Here the brain interprets the electrical signal and re-adjust the image upward allowing us to “see” the object. Hence, sight (vision) is achieved in the brain.
Did You Know ? 
- Human Eye Facts
- Animal Eye Facts


 R. Edmondson
United States
R. Edmondson
United States











































12 Comments:
I found that babies initially see the world upside-down to be really interesting!
Thanks for the excellent info!
Furkids:
You are welcome :)
Take care.
I love visiting your site and learning new things. Keep up the great work!
See ya! :-)
Hey, very informative indeed. I like it!
Chench:
Thanks for the compliment and encouragement. I am very grateful that you find this site educational!
Have a great day and catch you later :)
Peace:
Thank you very much! The funny thing is that I am just coming from your site and here you are:)
I am blind for 15 years I paint pictores. I now relize tyhe brsain records more that you think, to be retrived, at a later date I still see
Isn't it interesting how those that lose their eyesight adapt by having their remaining senses become more accute?
Scientists recently showed that those that are blind use their brain differently; the sense of touch, for example, fires off much quicker to the brain...and in a way, blind people create a new type of vision, using their "mind's eye."
Puremood:
Thanks for the compliment and I am glad that you found this post useful for your kids :)
Bye for now.
Lloyd:
Thanks for the comment and for stopping by.
The brain is like a computer it collects information (data) that it receives through our five senses and store them to be retrieved at a later date when it is needed. So, if you are not able to see for any reason then the brain will always retrieve those information from your memories of past experience in your life.
Phoenix :
Thanks for stopping by and leaving an interesting comment that always compliment my articles. I see that you are a science enthusiast like myself :)
The brain is the most complex organ you possess that will react and respond accordingly to any given situation that might put us at a disadvantage in our environment. This therefore goes for our five senses. If one of our senses is seriously affected then the others become heightened to makeup for that one which is lost thus, increasing the survival of that individual in his environment. These other senses will be relied upon greater and will therefore be more acute above those persons that have all five senses working properly.
What is your source for the babies seeing the world upside down fact. I just "learned" that yesterday and want to know if it is really true.
marion & mae ann says that...
thanks for the information!.. until nxt tym !! bye2
Thanks you. Very good post.Unless they can offer a really compelling reason for users to come back, it will be the next Bebo, MySpace
I use my eyes every day and I didn't even know most of these facts. Not only did I have fun reading them, but I've also learned a lot out of it.
Post a Comment
<< Home