 The Skin: The organ used by the body for touching is the skin and it is the largest sensory organ of the body containing more than 4 million sensory receptors. It is the outer body covering of animals (vertebrates - animals that have a backbone). The skin consists of four distinct layers: the epidermis, the basement membrane zone, the dermis and the subcutaneous layer. It is a delicate and resilient organ that constantly renews itself and contain many specialized cells and structures that are essential to our survival.
The Skin: The organ used by the body for touching is the skin and it is the largest sensory organ of the body containing more than 4 million sensory receptors. It is the outer body covering of animals (vertebrates - animals that have a backbone). The skin consists of four distinct layers: the epidermis, the basement membrane zone, the dermis and the subcutaneous layer. It is a delicate and resilient organ that constantly renews itself and contain many specialized cells and structures that are essential to our survival.Click to enlarge image
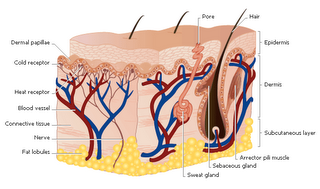 Many of the functions carried out by the skin that are essential to our survival include:
Many of the functions carried out by the skin that are essential to our survival include:- Physical barrier - It protects the vital organs inside the body against friction, shearing forces and damaging ultraviolet rays of the sun.
- Regulate body temperature - maintaining the proper temperature for the body to function excretes some waste products - through sweating.
- Prevent harmful microorganisms and chemicals from entering the body
- Protection - prevent against harmful: microorganisms (infections), chemicals, ultraviolet irradiation from the sun, foreign particles.
- Ultraviolet-induced synthesis of vitamin D - synthesizes the production of vitamin D that helps metabolize calcium and phosphorous, which is important for healthy bones and teeth.
- Prevention of excessive water loss or absorption.
- Wound healing - has the ability to repair itself after injury.
- Sensory organ - contains various types of specialized nerve cells responsible for the sense of touch.
Sense of Touch

 Touch is the first of the five senses to develop in the womb and thereon plays an essential role in our everyday life and even to our own very existence. Through the sense of touch we can detect different textures and temperatures of different levels. Our skin allows us to detect if something is squishy, wet, slimy, smooth, rough, hard, soft, fluffy, spiky, ridged, hot or cold and even by how much in relations to our body temperature. Our skin containing sensory receptors also allows us to identify several distinct types of sensations (stimuli) such as tapping, vibration, pressure, pain, heat, and cold. By detecting textures and sensations this helps to protect us from serious physical bodily harm through our daily contact with our surrounding by sending us important information about the environment. One example of such sensation is pain. This sensation serves as an warning (alert) system that indicates to us that something is seriously wrong with our body or that there is something doing harm to our body (see: The Purpose of Pain).
Touch is the first of the five senses to develop in the womb and thereon plays an essential role in our everyday life and even to our own very existence. Through the sense of touch we can detect different textures and temperatures of different levels. Our skin allows us to detect if something is squishy, wet, slimy, smooth, rough, hard, soft, fluffy, spiky, ridged, hot or cold and even by how much in relations to our body temperature. Our skin containing sensory receptors also allows us to identify several distinct types of sensations (stimuli) such as tapping, vibration, pressure, pain, heat, and cold. By detecting textures and sensations this helps to protect us from serious physical bodily harm through our daily contact with our surrounding by sending us important information about the environment. One example of such sensation is pain. This sensation serves as an warning (alert) system that indicates to us that something is seriously wrong with our body or that there is something doing harm to our body (see: The Purpose of Pain). Touch (sensory) receptors let us also experience the awesome feeling of beauty in nature and in our loved one's. We can feel the warmth of the sun’s ray on our skin and you can feel the gentle blowing of air caressing your body. One can also feel the awesome and delightful experience of your wife or husband reaching out and touching you, kissing you, and caressing you. You can imagine the gentle action of his/her fingers tracing all the smoothness and warmth of every surrounding and curves that makes up your personal frame that you call your body. The sense of touch (as do all the other four senses) gives us the gift to experience and express our love for each other. What an awesome and wonderful gift that just reading or thinking about it alone should cause goose bumps to rise freely on your skin. Our sense of touch is so very important
Touch (sensory) receptors let us also experience the awesome feeling of beauty in nature and in our loved one's. We can feel the warmth of the sun’s ray on our skin and you can feel the gentle blowing of air caressing your body. One can also feel the awesome and delightful experience of your wife or husband reaching out and touching you, kissing you, and caressing you. You can imagine the gentle action of his/her fingers tracing all the smoothness and warmth of every surrounding and curves that makes up your personal frame that you call your body. The sense of touch (as do all the other four senses) gives us the gift to experience and express our love for each other. What an awesome and wonderful gift that just reading or thinking about it alone should cause goose bumps to rise freely on your skin. Our sense of touch is so very important yet we usually take it for granted! A blind person makes much use of his/her sense of touch to move around and to read - raised type characters (Braille)- with their fingers. The most sensitive touch (tactile) receptors can be found at the back of your neck, your face, lip, tongue, upper arm, fingers, chest, soles of your feet, and between your legs. The Sense of Touch let us experience the sensation (feel), shape and size of objects in our surroundings.
yet we usually take it for granted! A blind person makes much use of his/her sense of touch to move around and to read - raised type characters (Braille)- with their fingers. The most sensitive touch (tactile) receptors can be found at the back of your neck, your face, lip, tongue, upper arm, fingers, chest, soles of your feet, and between your legs. The Sense of Touch let us experience the sensation (feel), shape and size of objects in our surroundings.How we feel things around us
The human skin contains various kinds of sensory receptors (specialized nerve cells) that are widely dispersed throughout the body. These sensory receptors based on their type and function carry out various mechanical, thermal, or chemical stimuli. Whenever one or more of these nerve endings of the sensory receptors in the skin are stimulated by a stimuli (e.g heat, cold, vibration, pressure) it results in the release of certain "stimuli message(s)" that is sent to the brain for processing and reaction.
When a sensory receptor is stimulated by a stimulus it releases a “message” that is converted into an electrical signal (impulse). This electrical impulse (message) is then taken by the Sensory neurons (a nerve cell that carries impulses to the Central Nervous System) from the receptors through the peripheral nervous system (various nerves branch out to the entire body) and into the central nervous system (spinal cord and brain). When the message leaves the spinal cord it is then taken to the brain where it analyzes the signal (message) and registers the effect of the stimulus then take the appropriate response. If a stimulus (e.g. a normal pressure or vibration from a touch) is a harmless one, then the brain would response accordingly based on its interpretation of the message received from the sensation from the sensory receptor - whether it be the need to laugh, smile, be in awe, be attentive etc. The way the brain interpret (understand) sensations in our lives will also be shaped by our previous experiences that are stored inside our brains. This goes for both internal and external environmental conditions.
Using the stimuli heat as an example, when one places their finger or other parts of their body on a hot object, our pain receptors are stimulated by this extreme heat stimulus and release a “pain message” that is converted into an electrical signal (impulse). This electrical impulse ( pain message) will then follow the route explained above. However, since this stimulus is very harmful a quick response is required to prevent serious injury to the finger or whatever part of the body it is. In this case, the pain message coming from the receptor will need a fast response that will take place in the spinal cord, before it goes to the brain to be filtered and analyzed before an action is taken. This quick response process in the spinal cord is called the reflex arc. Reflex arcs provide a means for immediate response (withdrawal) from the harmful stimuli. This means an unconscious reflex action takes place before the pain signal reaches the brain where it is perceived at a conscious state. Immediate (rapid) response that is processed in the spinal cord is very important in order to save serious damages to be done by a stimuli such as that of extreme heat or a sharp object.
 Diagarm showing reflex arc {click to enlarge}
Diagarm showing reflex arc {click to enlarge}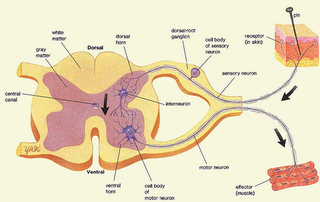 Diagarm showing a detail view of reflex arc {click to enlarge}
Diagarm showing a detail view of reflex arc {click to enlarge}A response message coming from the brain and spinal cord (Central Nervous System) is taken by the motor neurons (a nerve cell that carries impulses “messages” away from the CNS) to the effectors (muscles) and glands. Here they tell the appropriate muscles to contract in order to withdraw from the stimuli. If it is not harmful stimuli then the brain will interpret (understand) and respond in similar or some another way. For example, if the stimuli or stimulus gives a sensation that you might find soothing or pleasant then the understanding of the message in your brain will let you respond accordingly by relaxing muscles in your face and or increase your heartbeat, release hormone from a specific gland and other such conditions depending on how the brain analyzes the information for a given situation.
Related Articles:
How are we able to see things?
Does Pain Serve a Purpose?
I LOVEEEEEDDDDDD IIIIIIITTTTT!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!! <3 <3<3<3<3
ReplyDeleteNo life -_-
ReplyDeleteI was madly searching for this information... Thank You :)
ReplyDeletewho wrote this article?
ReplyDeletenice information
ReplyDeletethis is amazing i don't even have to use another source! but seriously that must of took a looonnng time! get it?
ReplyDeleteMy god i been looking for information
ReplyDelete4 ever T`T thxz alotzzz o 3o
~Darkesttaco