Can you hear sound in space?
 Did you know that you can not hear sound in space, as we do here on Earth? If not, you are in for a surprise! Most people do believe that sound can be heard in space. This myth of sound in space, is spread mostly by Hollywood space movies and also by TV. Why do they do this? The reason why this is done is that, sound effects and music greatly enhance the psychological effects that movies have on an audience thus, making the movie a lot more interesting and entertaining. So, if a film maker take the risk of eliminating some of the cost of their sound technicians job, most likely it can back fire and eliminate some of their profit. Nobody wants to watch a space action movie without the sound. It would make the movie very boring.
Did you know that you can not hear sound in space, as we do here on Earth? If not, you are in for a surprise! Most people do believe that sound can be heard in space. This myth of sound in space, is spread mostly by Hollywood space movies and also by TV. Why do they do this? The reason why this is done is that, sound effects and music greatly enhance the psychological effects that movies have on an audience thus, making the movie a lot more interesting and entertaining. So, if a film maker take the risk of eliminating some of the cost of their sound technicians job, most likely it can back fire and eliminate some of their profit. Nobody wants to watch a space action movie without the sound. It would make the movie very boring.
First, in order to explain space and sound, you will need to know the three states in which all matter exist. For sound to travel, it will always need a medium to travel through. These medium are the three states of matter: solid, liquid and gas. Sound travels in different ways depending on the medium.
===============================================
: If you are knowledgeable about matter, atoms, molecules, intermolecular forces and their behavioral properties, then you can scroll down and start at: What is sound? If you are also knowledgeable about sound, then you can scroll down and start at the heading: Outer space.
===============================================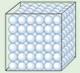 Solids contain particles that are attracted to each other by strong forces. These forces cause the particles to arrange themselves in a closely packed pattern. These particles vibrate, but do not change position. The attractive forces among the particles of a solid are strong enough to hold these particles together in a fixed position within the solid and thus maintain the solid in a definite shape.
Solids contain particles that are attracted to each other by strong forces. These forces cause the particles to arrange themselves in a closely packed pattern. These particles vibrate, but do not change position. The attractive forces among the particles of a solid are strong enough to hold these particles together in a fixed position within the solid and thus maintain the solid in a definite shape.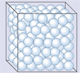 Liquids contain strong forces of attraction between their particles. They are closely packed but not in a pattern. These particles are constantly moving and so the particles change their position. The attractive forces among the ultimate particles of a liquid are sufficiently strong enough to hold them together but are not strong enough to hold them in a fixed position.
Liquids contain strong forces of attraction between their particles. They are closely packed but not in a pattern. These particles are constantly moving and so the particles change their position. The attractive forces among the ultimate particles of a liquid are sufficiently strong enough to hold them together but are not strong enough to hold them in a fixed position.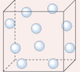 Gases have weak forces of attraction between the particles. These particles have a lot of kinetic (movement) energy. They are in constant random motion. The particles are far apart (essentially independent of each other) and are not fixed in a pattern. Thus , gas is everywhere.
Gases have weak forces of attraction between the particles. These particles have a lot of kinetic (movement) energy. They are in constant random motion. The particles are far apart (essentially independent of each other) and are not fixed in a pattern. Thus , gas is everywhere.
Note:
Atoms and molecules are attracted to each other as a result of different intermolecular forces.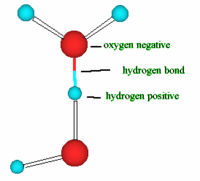 Some example of these intermolecular forces are: hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, covalent bonds as well as other forces. For atoms and molecules that have relatively small amounts of energy (kinetic energy) they will have less energy to move around and therefore less interaction between them. They will be more under the restriction of the attracting forces between their atoms or molecules. For those with higher energy of motion they will move about more quickly overcoming some of these attracting forces between them. Hence, the more energy a substance has, the more molecular movement that is taken place.
Some example of these intermolecular forces are: hydrogen bonds, van der Waals forces, covalent bonds as well as other forces. For atoms and molecules that have relatively small amounts of energy (kinetic energy) they will have less energy to move around and therefore less interaction between them. They will be more under the restriction of the attracting forces between their atoms or molecules. For those with higher energy of motion they will move about more quickly overcoming some of these attracting forces between them. Hence, the more energy a substance has, the more molecular movement that is taken place.
Explanation of Matter in relationship to sound wave
Solids
Particles in solids do not move about because they are closely packed and held together by strong intermolecular forces. Therefore, they can only vibrate in a fix position, sending sound waves along its path very fast. This is similar to a domino effect.
liquids
Particles in liquids are not as closely packed as that of solid so, they can also vibrate and collide with other of their particles over a short range; sending sound waves through it. These particles can only move over a short distance because of the force of attraction between molecules. These forces provide the molecules to move over a short range while sufficiently strong enough to hold them together.
Gases
Particles in gases are very far apart from each other. They can vibrate as well as move freely and randomly in all direction. This is due to the fact that the force of attraction between the particles are negligible. This means, there is no force of attraction between gas particles. Therefore, since gas particles are very far apart , sound wave traveling through this medium, will be much slower than that of a liquid and a solid respectively. Because of gas particles being everywhere on Earth, we can hear sound from all directions. ( Further down you will learn how sound travels through air)
Sound is a series of mechanical compressions and rarefactions or longitudinal waves that successively pass through a medium (solid, liquid or gas ). In sound waves parts of matter (molecules or groups of molecules) move in a direction of the spreading of the disturbance (as opposite to transversal waves).
Simplifying this definition to soundwave in air:
Sound is the movement of air particles created by a vibrating source. A vibrating source can be sound coming from a drum, speaker of a radio, the mouth of a person (vocal chord), a car engine, a plane above the sky and so on.
The movement of air particles move in a series of wave (longitudinal wave) which are caused by the collisions between the air particles ( compression and rarefaction) as they move away from the vibrating source.
CLICK THE FIRST IMAGE BELOW TO SEE HOW THE PARTICLES MOVE.
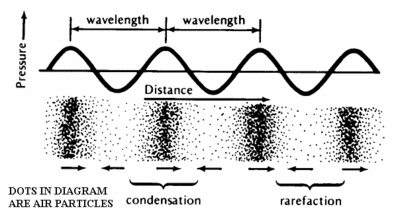
Compression ( condesation) and rarefaction mean, in simple terms, that the air particles moves in a to and fro position where they collide with each other to form a cluster (compression) then they rebounded from each other, the same effect of hitting a ball against a wall (rarefaction). This sound will be carried this way by the air particle in a outward fashion similar to ripple in a pond as it continue to collide with air particles. The air particles do not move over a large area but, carry the sound by colliding with other air particles. This way it passes on the vibration similar to a domino effect, as it moves away from the vibrating source.
Sound being a longitudinal wave, can be reflected from the surface of an object. This is why we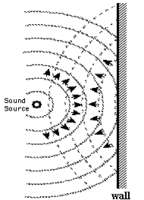 hear sounds around corners. Although sound is commonly associated in air, sound will readily travel through many materials. However, there are insulating materials that absorb much of the sound waves, preventing the waves from penetrating the material or being reflected from it surface (echo). These type of material is used in studios to prevent interference from unwanted sound entering or preventing an echoing effect from sound already being produced.
hear sounds around corners. Although sound is commonly associated in air, sound will readily travel through many materials. However, there are insulating materials that absorb much of the sound waves, preventing the waves from penetrating the material or being reflected from it surface (echo). These type of material is used in studios to prevent interference from unwanted sound entering or preventing an echoing effect from sound already being produced.
While sound will readily travel through many materials, in order for us to hear it, it will have to travel through the air to reach our ear (eardrum). Your eardrum vibrates from sound waves to allow you to sense them. We might be able to detect it through vibration of solids, the ripple in liquid but you can only detect it in air by hearing it. Inspite of this, humans can not hear all sounds that travel through the air. It will have to be at a certain decibel for us to hear it. For e.g. dogs can hear sounds that are not able to be detected by humans.
Sound can also be detected by other means other than hearing it. Sounds traveling in any of the three state can be detected using electronic detectors. E.g Microphones
Outer space Outer space is define as: all space in the universe beyond Earth and its atmosphere, especially interplanetary and interstellar space, but including the region where astronauts walk and satellites orbit the Earth.
Outer space is define as: all space in the universe beyond Earth and its atmosphere, especially interplanetary and interstellar space, but including the region where astronauts walk and satellites orbit the Earth.
In outer space, there is no air (atmosphere) and because of this, sound will not be able to travel from a vibrating source to any other region in space. This is why astronauts have to wear special suits carrying air (oxygen) supply for breathing. Therefore, since there is no air in space, there will be no medium for sound to travel. Hence, no sound will be heard in space because it is a vacuum. (Continue to read to learn how Astronaunt coummunicate in space!)
Did You Know Questions and Answers
Is outer space a total vacuum?
Space contains tiny particles called cosmic dust and elements like hydrogen and helium atoms. However, the vastness of space not having any beginning or end, has unimaginable distances between stars, planets and galaxies. Therefore, having a few hydrogen and helium atoms for every cubic meter (or per cubic centimeter) space is virtually a vacuum.
However, the vastness of space not having any beginning or end, has unimaginable distances between stars, planets and galaxies. Therefore, having a few hydrogen and helium atoms for every cubic meter (or per cubic centimeter) space is virtually a vacuum.
Does sound travel in space?
Space being nearly perfect vacuum, sound waves can not travel from its source through the vacuum to another point in space or to the ear of an individual. In order for one to hear sound it must travel through gas particles which space has very few per cubic centimeter. This is very much less than that in the Earth’s atmosphere. Hence, space is silent.
Is there sound in space?
In space movies, you will hear spaceships exploding, spaceships engine giving off sounds, sounds of firing guns etc. but, as you should know by now, sound can not travel in space. That means, if an explosion should take place in space, similar to a distance here on earth, you would not be able to hear it. This also goes if you are very close to the explosion ( before you are incinerated that is). So, is there sound in space? In space there are sound sources (e.g. explosion of stars, collision of asteroids and so on) but they do not (and cannot) travel to be detected. However, sounds can travel by air in the spacecraft through the metal of the ship. You can hear sounds in the spacecraft only due to air particles inside.
explosion should take place in space, similar to a distance here on earth, you would not be able to hear it. This also goes if you are very close to the explosion ( before you are incinerated that is). So, is there sound in space? In space there are sound sources (e.g. explosion of stars, collision of asteroids and so on) but they do not (and cannot) travel to be detected. However, sounds can travel by air in the spacecraft through the metal of the ship. You can hear sounds in the spacecraft only due to air particles inside.
Technically, if you are in a spaceship and it explode, you would hear it before you die due to the air particles in the ship. Likewise, if another spacecraft was to explode not far from your ship, objects flying from that ship would hit your ship sending sound wave through the ship structure by vibration. This vibration would then be passed on to the air particles in your ship thus, causing you to hear it. Also, the exploding ship would release gasses that allow sound to travel along its part but, this would very quickly diminish since the gas particles would readily spread out in the vastness of space (losing its density). Therefore, sound would die very quickly over a very very short distance and any sounds carried by the gases from the explosion, would still be too faint for you to hear it in your space ship. So, strictly speaking, in this case it is possible for sound to travel a very very short distance but all in all, space is silent.
the air particles in the ship. Likewise, if another spacecraft was to explode not far from your ship, objects flying from that ship would hit your ship sending sound wave through the ship structure by vibration. This vibration would then be passed on to the air particles in your ship thus, causing you to hear it. Also, the exploding ship would release gasses that allow sound to travel along its part but, this would very quickly diminish since the gas particles would readily spread out in the vastness of space (losing its density). Therefore, sound would die very quickly over a very very short distance and any sounds carried by the gases from the explosion, would still be too faint for you to hear it in your space ship. So, strictly speaking, in this case it is possible for sound to travel a very very short distance but all in all, space is silent.
How Astronauts communicate in space? Astronauts communicate with each other in space, when they are spacewalking, through the use of radio wave. Radio wave signal is sent to their headsets which then translate the signal into the form of sound . When receiving and sending message to earth it is sent in the form of radio wave which is then translated to sound wave (message) by a radio set. Radio wave is a part of the light spectrum called electromagnetic spectrum ( see diagram below) and is therefore a light wave. Light does not need a medium to travel and this, further explain why the Sun’s light travel through space to earth. Light waves are not sound wave.
Astronauts communicate with each other in space, when they are spacewalking, through the use of radio wave. Radio wave signal is sent to their headsets which then translate the signal into the form of sound . When receiving and sending message to earth it is sent in the form of radio wave which is then translated to sound wave (message) by a radio set. Radio wave is a part of the light spectrum called electromagnetic spectrum ( see diagram below) and is therefore a light wave. Light does not need a medium to travel and this, further explain why the Sun’s light travel through space to earth. Light waves are not sound wave.
Astronauts can however, talk to each other as if they were on Earth only when they are in their space ship. Here, there are enough air particles to vibrate and take the sound to their ear drum.
 On Earth air (gas) particles are everywhere, a big layer of gases that surrounds the Earth called the ATMOSPHERE. This allow sounds of all kind to travel in all direction over the earth. Gases are random moving groups of atoms.
On Earth air (gas) particles are everywhere, a big layer of gases that surrounds the Earth called the ATMOSPHERE. This allow sounds of all kind to travel in all direction over the earth. Gases are random moving groups of atoms. A summary of the things you should know about sound.
A summary of the things you should know about sound.
1. All sound requires matter through which to travel. This is why sound does not travel in space (vacuum).
2. Sound waves do not travel in straight lines. This is why you can hear some one calling your name whether you are in front, behind, beside or above that person who is the source.
3. Sound wave can be reflected. This is why you can hear sounds around a corner and also is the reason why you hear echo.
4. The speed of sound waves usually increases with increased temperature. This due to the molecules and atoms gaining more energy (kinetic energy) to move more faster taking the vibration a way from the source.
5. Sound travels fastest through a solid and slowest through a gas. The more densely packed the molecules of a substance are, the faster sound will travel through that substance.
6. The speed of sound is quite slow compared to the speed of light. This is why you see the lighting in a thunderstorm before hearing the thunder.


 R. Edmondson
United States
R. Edmondson
United States




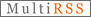







































11 Comments:
My goodness... that was quite a read! Thank you for that interesting science lesson!
Also, thank you for commenting on my site!
This is KnowledgeBlog.
Thank you Prof for that piece on Sound and Space.
I learnt something new on it.
As far as the Hollywood sound effects in space, this was addressed as far back as the original "Star Trek" series. For the opening shots (but not the intro theme) where the U.S.S. Enterprise may orbit a planet, it was decided to use no sound effects because there would have "really" been no sound in space. So, as hokey as the original series may have been, they strove for some realism!
Thanks for stopping by my blog and commenting from time to time.I hope you are still writing your blog in about 10 years when the Branch and the Blossom need to do research for school!
Junebee(former Trekkie!)
Very good article on sound and space.
I think I remember one movie that used the fact there was no sound in space for a space walk scene.
It was dead silent until the man came into the airlock and then the air and sound rushed in.
(I confess I didn't read the whole article, but I did read alot of it :) )
Of course I knew "in space no one can hear you scream" I read it on the first Alien movie poster.
Nice subjects.
You are assuming that air is the only gas that can transmit sound. The hot gasses from explosions or propulsion carry energy, and if these gasses are incident with an eardrum or microphone diaphragm they will 'sound'.
Now, as for the laser beams, perhaps those are not supposed to be heard :)
i dont want to sound critical, but scientists have discovered that sound can come from space. As you said space is almost a perfect vacuum. The small amounts of gas in space is enough to carry sound which travels at 300km/sec. NASA detected a B flat coming from a black hole 250 million light years away. Yes you cannot hear sound in space with human ears. But sound can be detected from large NASA satellite dishes.
Thaank you! I knew most of that, but some of it suprised me. That was very interesting, and it helped a lot for what I'm working on in my novel. It's a fiction novel, but I want all the scientific facts to be correct. Thanks again! :)
There is sound is space, check it out on google. Space is full of particles and the sound waves travel via them. Speed of sound is space is ~400km/sec
Actually in space, the interplanetary medium is a very dilute gas at a density of about 10 atoms per cubic centimeter, and the speed of sound in this medium is about 300 kilometers/sec. Typical disturbances due to solar storms and 'magneto-sonic turbulence' at the earth's magnetopause have scales of hundreds of kilometers, so the acoustic wavelengths are enormous. Human ears would never hear them, but we can technologically detect these pressure changes and play them back for our ears to hear by electronically compressing them.
What you are talking about are radio waves that are being intercepted and translated into sound using machines. Gaseous particles in space simply aren't close enough to one another to interact at all.
Post a Comment
<< Home